7. PRESSURE
Pressure is the force (f) acting normally per unit area (A).
i.e The word normally means perpendicular.
Mathematically;
The SI units of pressure are N/m2 or Pascal.
Example.
1. Find the pressure exerted when a force of 640N acts in the area of 16m2
Data:
Force (f) = 640N
Area (A) =16m2
Pressure (p) =?
Solution:
Pressure=40 Pascal
2. A pressure of 75N/m2 is resulted from a certain force acting on an area of 0.8m2. Calculate its force acting on it.
Data:
Pressure = 75 N/m2
Area = 0.8m2
Force =?
Solution
F = PA
: F = 75N/m2×0.8 m2
= 60N
3.Find the pressure exerted when a force of 3600N act on the area of 36m2
Data:
F = 3600N
A = 36m2
P =?
P = 100N/m2
Maximum and minimum pressure
Maximum pressure is the value of high pressure and it is determined when a force acts perpendicular.
Example
1. A body of area 0.5m2 and 20m2 acts on a force of 4000N. Calculate the maximum and minimum pressure.
Data:
Area minimum (A1) = 0.5m2
Area maximum (A2) = 20m2
Force F = 4000N
Maximum pressure =?
Minimum pressure =?
Maximum pressure = 8000N/m2
Minimum pressure = 200N/m2
2. A body of area 0.024m2 and 15m2 acts on a force of 3600N.Find the minimum and maximum pressure given:
Force = 3600N
Area 1 = 0.024m2
Area 2 = 15m2
Maximum pressure =?
Minimum pressure =?
The maximum pressure = 150,000Pascal
The minimum pressure = 240 Pascal
1. The body which weights 500N covers an area of 250m2 . Find the pressure which is exerted on the flour.
Given data
Force F=500N
Area A=250m2
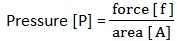
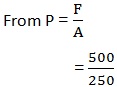
= 2N/m2 or 2 Pascal
CONDITIONS FOR PRESSURE
Pressure depends upon the area. I.e.: The smaller the surface area the greater the pressure and the vice verse. For example it is easy to cut meat with a sharp knife than with a blunt one, this is because in the sharp the area is small than in the blunt one.
APPLICATION OF PRESSURE
a) Solids
-
Broad tire of a tractor.
-
Potters with a heavy load on the back in order to reduce pressure.
-
The use of different edges of knives.
b) Liquids - Variation of pressure with depth.
- Liquid pressure varies with depth. For example; the higher the depth the greater the pressure.
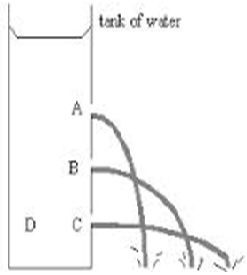
Water is pushed through the holes of different speed. The speed at A is higher than the speed at B and C. The speed at C is very less as compared to the speed at B and A. For example pressure in a liquid increases with the increase in depth.
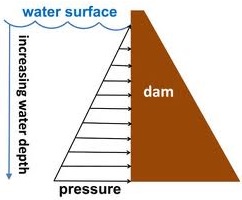
The wall of the dam is made thicker at the bottom because pressure is greater at the bottom.
Example 2
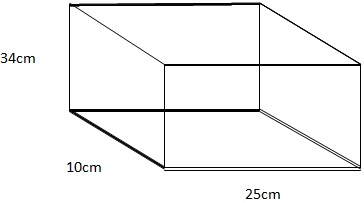
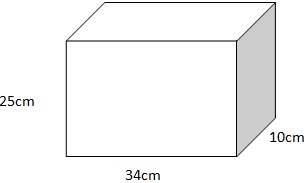
A rectangular block weighing 250N has dimensions 34cm, 25cm by 10cm what is the greatest pressure and the least pressure it can exert on the ground
Solution
a) The greatest pressure the block can provide when it is resting on a horizontal flour occurs when it rests on its smallest face i.e. the smaller the area the larger the pressure
The smallest surface area is 0.25m x 0.1m=0.25m2

= 1000 Pascal
b) The least pressure that the block can produce when resting on a horizontal floor occurs when it rests on its largest face i.e. The larger the area corresponds to its least pressure
Largest surface area 0.34m x0.25m=0.085m2

= 2941.18
PRESSURE IN LIQUIDS
The pressure under width, The higher , the depth, the higher the pressure and the low the depth, the lower the pressure.
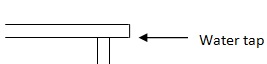
EXPERIMENT
AIM
To demonstrate the increase of pressure with depth.
MATERIALS
The apparatus to be used and they include the following;
-
A tall vessel
-
Water tap

PROCEDURE
-
Take the vessel
-
Make three holes on its side
-
Fill the vessel with tap water
OBSERVATION
- Water is pushed through the holes at different speeds.
- The pressure at the hole A is greater than that at hole C because of the difference in height.
PRESSURE FORMULA
Consider a liquid columns standing on an area X at a depth “h” with liquid of density "D".
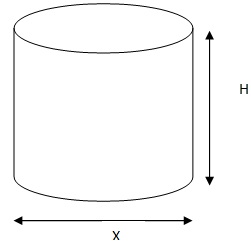
The pressure P exerted by this column of liquid is given by;
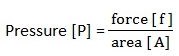
But force = Mass x Acceleration due to gravity,
Mass = Density X volume,
Volume = Area x height,
Volume = A.h, then mass = A.h
Force weight = A.h x g
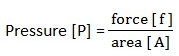
Therefore
Pressure in liquids = Density X Acceleration due to gravity X height
Example:
1. If the cube of the height 4m contains water of density 1000kg/m3. Calculate the pressure exerted by taking g = 9.8N/kg
Solution
Data given
(h) Height = 4m
(D) Density = 1000kg/m3
(g) Gravity = 9.8N/kg
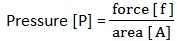
P = density x height x gravity
P = 1000 x 4 x 9.8
P = 39 200N/m3
2. The pressure at the base of the cube is 98,000N/m2. Find the height of the cube if the density of water is 1000kg/m3 and g = 9.8N/kg.
Solution
Data given
P = 98000N/m2
D = 1000kg/m3
g =9.8N/kg
But pressure is given by P=h.g
h =?
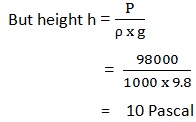
LIQUID FINDS ITS OWN LEVEL
When water is poured into a communicating tube, even if each part has different cross section area and shape, the water will be at the same level.
The principle of the spirit level
A spirit level is an instrument used by masons to test whether the surface is level.

When the surface is horizontal the spirit level in both limbs A and B is the same.
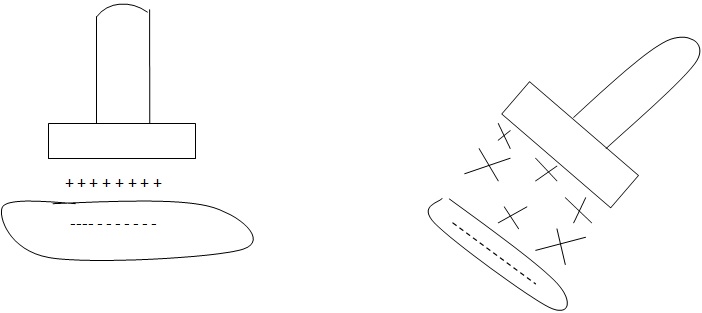
ACTION OF PRESSURE IN LIQUIDS
To a non-viscous liquid in an enclosed vessel e.g. a ball
If it is compressed the pressure is transmitted equally in all directions.
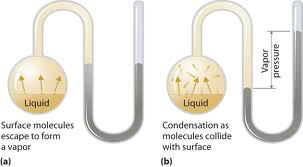
When the ball is squeezed, water will come out equally in all directions.
PRINCIPLE OF HYDRAULIC PRESS
Paschal's principle
If a liquid is filled precisely in vessel and pressure is exerted at one part of it, the effect of pressure will be transmitted equally throughout of total volume.
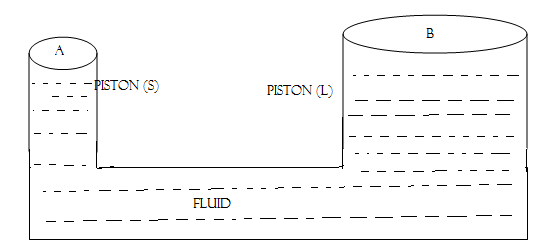
Pressure at piston (s )=
The effect to piston (L)
But F=?
F is the thrust due to P(s)
Hence therefore
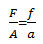
Example;
In the hydraulic system a body of 150kg need to be raised up at a thick column of 615.44cm2 cross-sectional area. If a narrow column has a 38.465cm2 find a minimum force should be applied.
Solution
Data
Mass= 150kg
Area (A)=615.4cm2
Small area (s)=38.465cm2
Minimum force =?
From
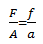

but F=Mg
f=93.7N
Therefore, a force 93.7N should be used.
Application of Pascal’s principle is applied mainly in:
-
Hydraulic press
-
Hydraulic brakes
MODES OF OPERATION
When a smallforce (f) is applied at S, the piston at area (d) produced some pressure.
The pressure (p) produced is transmitted through the liquid to the large piston at b.
A heavy load is raised by the force (f) by the pressure extended by small piston given by;
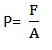
These pressures then produce a big force (f);
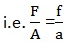
EXAMPLE
1. In a hydraulic press they area of a piston to which the effort applied is 5m2. If the press can raise a weight of 5KN of 2KN when and effort of 400N is applied. What is the area of the piston under the load?
Given data
a = 5m2
F = 2KN
f = 400N
A =?
APPLICATION OF HYDRAULIC PRESS
Hydraulic pressure is applied (used) in many area in our daily life.
Example;
-
In lifting heavy load i.e. in a crane.
-
In pressing cotton bale.
-
Shaping bodies of motor car.
-
Braking system of car.
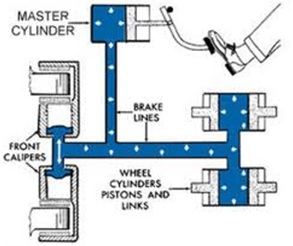
HYDRAULIC BRAKE
In modern cars there is braking system which slow each wheel equally. The system reduce the dangers of skidding off of the car. When the brake pedal is pressed, the pressure is transmitted through the liquid (oil) to the brake shoe where they are forced apart.
BRAKE SYSTEM
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
-
Air is matter and hence has weight
-
Air contains Oxygen, Hydrogen, carbon dioxide, helium etc.
-
Air exerts (pits) its weight onto the surface of the Earth.
Therefore atmospheric pressure is the weight which the layer rest on the earth surface.
Atmospheric pressure can be observed in several areas.
Example: -
-
-
-
In a glass tumbler
-
In a crashing can
-
-
In a glass tumbler when a glass is filled with water and covered with a card.
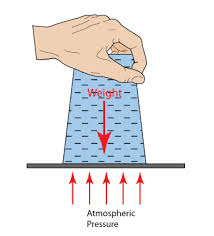
If the card and glass are turned upside down, the card holds in place, Because the upward force in air pressure is greater than the downward pressure.
CRUSHING CAN
Little water is put and boiled in an opened can, so that it drives off the air steam.

When heat is removed and the can is tightly, closed cold water is then poured into the can. The can is observed to collapse. When cold water is poured onto the can, the little steam inside condenses leaving vacuum. The outside pressure presses the can.
INSTRUMENT
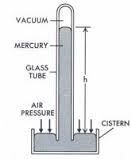
Atmospheric pressure is measured by Barometer
TYPES
There are three main types of barometer;
-
Simple Mercury barometer
-
Aneroid barometer
-
Fortin’s barometer
Advantages of barometer to another barometer (Aneroid)
-
It is used in confined space.
-
It is intact and portable.
-
It is used in aircraft i.e. it shows height where the plane is flying.
ANEROID BAROMETER -
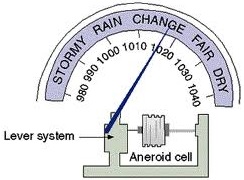
FORTIN’S BAROMETER
-
It is heavy barometer.
-
It is not portable.
-
It is very expensive (this is because it uses mercury in a liquid).
DEVICES WHICH WORK UNDER ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
They all work under the principal of siphon.
E.g.
-
Automatic flashing
-
Chain and bull flashing tank
-
Lift pump
-
Bicycle pump
-
Syringe
MERCURY BAROMETER