8. WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
WORK
Work is said to be done when the applied force produces a distance.
This work is the product of force (f) and distance (d) in the direction of force.
Therefore work is given by;
W = F.d
Where
F = force
d = distance
SI – UNIT OF WORK
The SI unit of work is given by;
W = F.d
F = Newton
d = Meter
SI- UNIT of work is Newton meter (Nm) or joule (J)
NB: 1 Joule of work is done when the force of one Newton (1N) is applied and moves a distance of one meter (1m)
Example
1. A sack of maize which weights 800N is lifted to a height of 2m. What is the work done?
Data
F = 800N
d = 2m
W =?
From
W = F.d
=800N x 2m
= 1600Nm
= 1600 Joule
ENERGY
Energy is the ability to do work.
SI – UNIT
The unit measure of energy is Joule (J).
THERE ARE VARIOUS FORMS OF ENERGY
e.g;
-
Heat energy
-
Sound energy
-
Solar energy
-
Nuclear energy
-
Electrical energy
-
Light energy
-
Mechanical energy
There are two types of mechanical energy;
-
Kinetic energy (K.E)
-
Potential energy (P.E)
-
KINETIC ENERGY
Is the energy possessed by a body due to its motion.
The kinetic energy is given by;
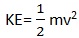
where m= mass
Areas where kinetic energy can be observed;
-
Moving cars
-
Walking people
-
People running
-
A moving train
-
A flying airplane
-
A moving ship
-
A jumping lion
-
A moving bicycle etc.
2. POTENTIAL ENERGY
This is the energy possessed by a body due to its state or position.
The potential energy is given by;
PE =m.g.h
Where
m = mass
g = gravity
h = height
The PE can be observed into the following areas;
-
A boy sitting on a bench
-
A pen put on the table
-
A man sleeping on a bed
-
A book placed onto a table
-
A ruler put on the table
-
A man standing on a bus stop
-
A brick put on the ground etc.
TRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY
The process whereby one form of energy is changed into another form of energy is called transformation.
-
The source of all energies is the sun therefore all energy is a result of the transformation of solar energy
Transducer - Is a device which is used to transform one energy to another
E.g;
-
Generator
It transforms mechanical energy to electrical energy.
-
Microphone
It transforms electric energy to sound energy.
-
Bulb
It transforms electrical energy to light energy.
The principle of conservation of energy it states that: - “Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but it can be transformed from one form to another”.
Example
1. A ball of mass 0.5kg is kicked vertically upwards and raised to a height of 5m. Find the potential energy required by the ball.
Solution:-
Given data
Mass=0.5kg
Height (h) =5m
P=m.g.h
P=0.5 x 9.8 x 5
=24.5 joules
POWER (P)
Power is defined as the rate of doing work.
Power (P) is given by;
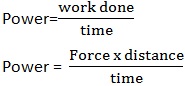
Therefore SI- UNIT of power is Watt
Example:
A boy lifted a box of 200N through the height of 3m in 5 seconds. Calculate the power.
Data
F= 200N
S= 3m
t=5s
P=?
Solution
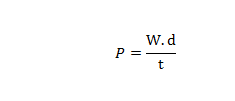
W.d= F×s
P= F×s/t
= 200N×3m/5
=120 Watt
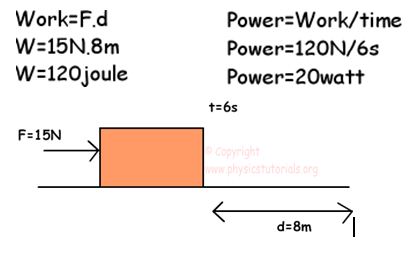
POWER
Power is the rate of work done in a unit of time. It can be misunderstood by most of the students. They think that more power full machine does more work. However, power just shows us the time that the work requires. For example, same work is done by two different people with different time. Say one of them does the work in 5 seconds and the other does in 8 seconds. Thus, the man doing same work in 5 seconds is more power full. The shorter the time the more power full the man. Let’s represent it mathematically;
The unit of the power from the equation given above, joule/s, however, we generally use the unit of power as watt.
1joule/s=1watt
Example: Find the power of the man who pushes the box 8m with a force of 15N in a 6seconds.
The power of the man is 20 watt. In other words he does 20 joule work in 6 seconds.