9. LIGHT
Definition
Light - is the form of energy which stimulates the sensation of vision or seeing.
The sun is one of the source of light energy.
Generally, the source of light is grouped (divided) into two main parts;
-
Natural sources
These are objects which produce their own light.
-Sun, stars, lightning
-
Artificial sources
These are objects which do not produce their own light.
-Electric lump, florescent tubes etc.
Concerning light there are two types of objects which provide light;
-
Luminous objects
These are objects which produce their own light.
E.g. Sun, stars
-
Non -Luminous objects
These are objects which do not produce their own light.
E.g. Moon and planets.
- Incandescent and Fluorescent
- These are artificial objects which release their own light due to effect of electricity or chemical reaction e.g -candle , Filament bulb, A gas filled tube light, A gas filled coil bulb.
PROPAGATION OF LIGHT
•Light travels in a straight line in a form of an arrow called a ray
A ray
A ray is the path taken by light.

Beam
A beam is a collection of rays.
There are three types of beam;
(I) Parallel beams/rays

(Ii)Converging rays
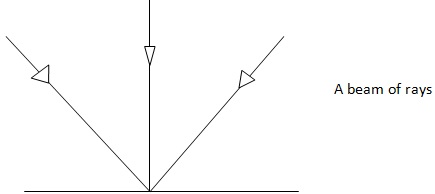
(Iii)Diverging rays
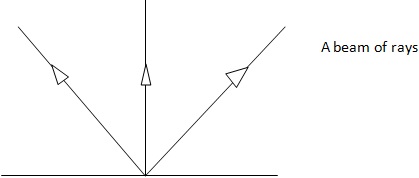
-
To verify that light travels in a straight line.
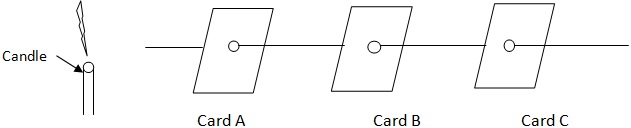
In the diagram
From card C we can see the candle;
-
If card B is put aside, the candle is not seen from C
-
This proves that light travels in a straight line.
TRANSMISSION OF LIGHT
This refers to the passage of light through objects.
Mainly there are three types of objects;
-
Transparent objects
Materials which allow the total amount of light to pass
E.g. Glass, air, pore, water etc
-
Translucent object
Materials which allow little amount of light to pass
E.g. Paper, tinted glass, plastics
-
Opaque materials
Materials which do not allow the passage of light
E.g. Stones, walls, wood, book etc
Usually opaque materials results to the formation of shadow.
SHADOW
A shadow is a part of surface which obstructed to receive light rays. Shadow gives the shape of a concerning objects.
Example;
When you walk in the open space during sunshine, you have to see a shadow shape like yourself is walking together for every step.
There are two types of shadows;
1. Umbra
Is a shadow of definite shape.
2. Penumbra
Is a shadow of indefinite shape.
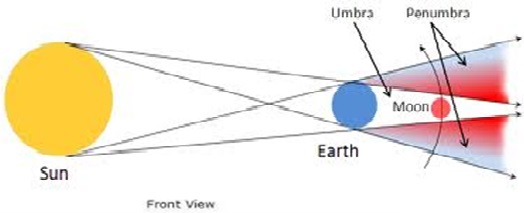
ECLIPSE OF THE MOON AND SUN
Eclipses that take place in these celestial objects as witnessed from the earth are caused or result of falling shadow at a particular surface.
1.SOLAR ECLIPSE
This occurs when the moon comes between the earth and the sun.
When the moon aligns between the sun and Earth, its shadow fall on the earth's surface. The observation of sun become abnormal; hence therefore we say eclipse of the sun. In so doing there is total eclipse of the sun and partial eclipse of the sun.
Partial eclipse of the sun
This is eclipse after falling of penumbra of the moon on the earth's surface.
Total eclipse of the sun
Is an eclipse which happen after falling of umbra of the moon on the earth's surface.
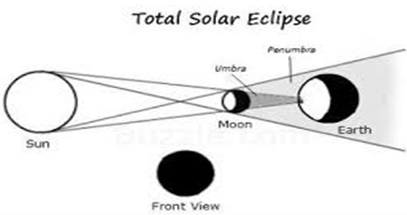
2.LUNAR ECLIPSE
This occurs when the earth comes between the sun and the moon.
Lunar eclipse happen when umbra or penumbra of the earth of on moon surface. In so doing, there is total lunar eclipse and partial lunar eclipse.
Partial lunar eclipse
Is an eclipse happen when penumbra of the earth fall on moon surface. The moon is observed in orange colour.
Total lunar eclipse
Is an eclipse happen when an umbra of the Earth fall on moon surface. The moon appear in red colour such that wet in the blood.
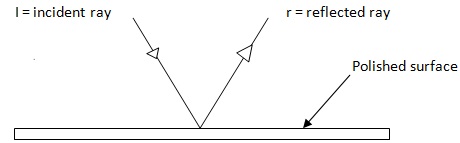
REFLECTION OF LIGHT
Definition: -
This is the bouncing back of light ray after reaching onto a smooth polished surface.
E.g. the surface of a metal, iron, copper, gold, mirror etc
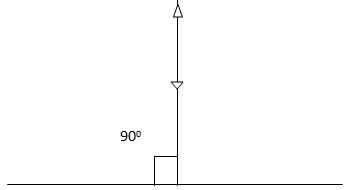
If a ray of light falls at 90° it will be thrown back in the same path.
There are two types of reflection;
i) Regular reflection
ii) Diffuse reflection
Regular reflection
Is the type of reflection where all rays are reflected in one direction. The reflected rays are also parallel to each other. It occurs when light is reflected on a smooth surface.
Regular reflection
Diffuse reflection (Irregular reflection)
Is the type of reflection where the reflected rays are not parallel. They are scattered. The image formed is distorted and this kind of reflection usually occurs on rough surfaces.
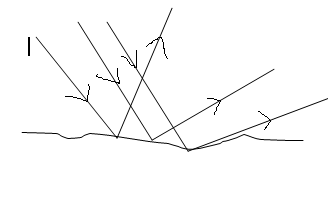
Diffuse reflection/Irregular reflection
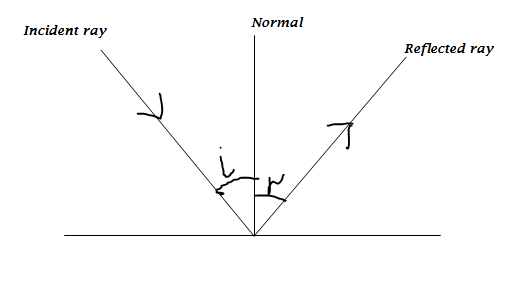
LAWS OF REFLECTION
First law
''The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal all lie on the same plane''.
Second law
''The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal''.
CHARACTERISTICS OF IMAGE BY A PLANE MIRROR
1. Image is virtual.
2. Image has the same size as that of the object .
3. The image has the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front the mirror.
4. Image is laterally inverted.
5. The image is upright (erect).
6.Laterally inverted
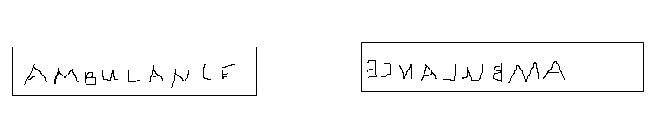
Laterally inverted
Magnification

REFLECTION ON THE TWO MIRRORS AT AN ANGLE
If the two mirrors are placed at an angle of 90°, the observer will see three images.
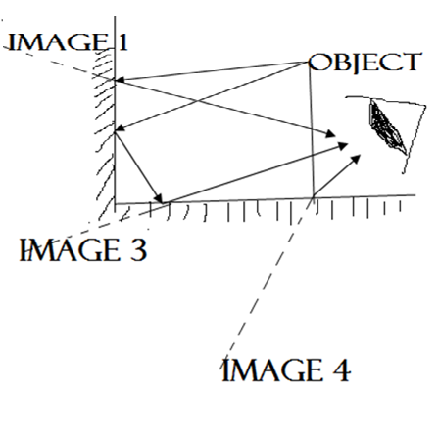
Multiple angles in in right angle mirrors
Generally, the number of images produced by two mirrors placed at an angle θ, is given by;
n= number of images
θ = angle between the mirror
However, if the angle between is 0º, the number of images will be infinity.
APPLICATION OF REFLECTION
1. Driving mirrors
2. Dressing mirrors
3. Mirrors in saloons
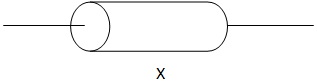
4. Periscope
A periscope is an instrument used to see over an obstacle from concealed position. The mirrors are placed at an angle of 45 as shown in the diagram below;
Simple periscope